Top 10 Nuclear Powers | Most Destructive Nuclear Weapons
Top Nuclear Weapons :-
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission bomb) or from a combination of fission and fusion reactions (thermonuclear bomb). Both bomb types release large quantities of energy from relatively small amounts of matter. The first test of a fission ("atomic") bomb released an amount of energy approximately equal to 20,000 tons of TNT(84 TJ). The first thermonuclear ("hydrogen") bomb test released energy approximately equal to 10 million tons of TNT (42 PJ).A thermonuclear weapon weighing little more than 2,400 pounds (1,100 kg) can release energy equal to more than 1.2 million tons of TNT (5.0 PJ).A nuclear device no larger than traditional bombs can devastate an entire city by blast, fire, and radiation. Since they are weapons of mass destruction, the proliferation of nuclear weapons is a focus of international relations policy.
HERE IS THE TOP 10 PICKS OF THE NUCLEAR WEAPONS THAT CAUSE A MASSIVE DESTRUCTION :-
1. Tsar Bomba (RDS-220 hydrogen bomb) – 50Mt
- The Soviet RDS-220 hydrogen bomb (code name Ivan or Vanya),Soviet Union is the origin of this weapon.It is known by Western nations as Tsar Bomba.
- TSAR BOMBA was the most powerful nuclear weapon ever created.It also remains the most powerful explosive ever detonated.The bomb had a yield of 58.6 megatons of TNT (246 PJ). In theory, it would have had a maximum yield of 100 megatons of TNT if it had included a uranium-238 tamper, but because only one bomb was built, this was never demonstrated.
- Tested on 30 October 1961.The single bomb was detonated at the Sukhoy Nos cape of Severny Island, part of Novaya Zemlya.
TESTING OF TSAR BOMBA :- http://festyy.com/wXEGtY
2.B41 nuclear bomb – 25Mt
- The B-41 (also known as Mk-41) was a thermonuclear weapon deployed by the United States Strategic Air Command in the early 1960s.
- It was the most powerful nuclear bomb ever developed by the United States, with a maximum yield of 25 megatons. The B-41 was the only three-stage thermonuclear weapon fielded by the U.S.
- It was based on the "Fagotti (bassoon)" test device first fired in the Redwing Zuni test of 27 May 1956
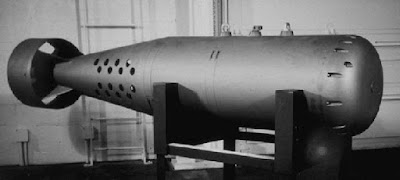
3.TX-21 "Shrimp" (Castle Bravo) – 14.8Mt
Image Credit :- Photovalet
- Castle Bravo Originted from The U.S.A.
- The device was the most powerful nuclear device detonated by the United States and its first lithium deuteride fueled thermonuclear weapon.Castle Bravo's yield was 15 megatons of TNT, 2.5 times the predicted 6.0 megatons, due to unforeseen additional reactions involving Li,which led to the unexpected radioactive contamination of areas to the east of Bikini Atoll.
- Castle Bravo was the first in a series of high-yield thermonuclear weapon design tests conducted by the United States at Bikini Atoll, Marshall Islands, as part of Operation Castle. Detonated on March 1, 1954.
TESTING OF CASTLE BRAVO :- http://festyy.com/wXEGZt
4.Mk-17/EC-17 – 10Mt to 15Mt
- The Mark 17 and Mark 24 were the first mass-produced hydrogen bombs deployed by the United States. The two differed in their "primary" stages. They entered service in 1954, and were phased out by 1957.
- The Mark 17 had a yield of 15 megatonnes of TNT (63 PJ).Total production of Mk 17s was 200, and there were 105 Mk 24s produced, all between October 1954 and November 1955. The Mark 17 and Mark 24 were identical in all respects save for the design of their primary section.They were the largest nuclear weapons ever put into service by the United States; only the Convair B-36 Peacemaker was capable of carrying them.
TESTING OF MK 17 :- http://festyy.com/wXEGN8
5.MK 24/B-24 – 10Mt to 15Mt
This is not the image of MK 24 But it was quit similar with this
- The Mark 24 nuclear bomb was an American thermonuclear bomb design, based on the third American thermonuclear bomb test, Castle Yankee. The Mark 24 bomb was tied as the largest weight and size nuclear bomb ever deployed by the United States, with the same size and weight as the Mark 17 nuclear bomb which used a very similar design concept but unenriched Lithium.
- Castle Yankee had a demonstrated yield of 13.5 megatons. The yield for the weaponized Mark 24 was predicted to be 10–15 megatons.
- The Castle Yankee thermonuclear test was the first bomb to use enriched Lithium-6 isotope, up to perhaps 40% enrichment (the earlier Castle Bravo test had used the same enriched lithium combination but was not weaponised i.e. was not built as a deployable bomb). The device tested was called the Runt II design; it was reportedly very similar to the Runt design tested in Castle Romeo, other than the enrichment level.
6.Ivy Mike H-Bomb – 10.4Mt
- The device was designed by Richard Garwin, a student of Enrico Fermi, on the suggestion of Edward Teller.Originted from the United States.
- The Ivy Mike test yielded an explosion of 10.4Mt, 700 times the explosive force of the weapon dropped on Hiroshima.
- Ivy Mike was the codename given to the first test of a full-scale thermonuclear device, in which part of the explosive yield comes from nuclear fusion. It was detonated on November 1, 1952 by the United States on the island of Elugelab in Enewetak Atoll, in the Pacific Ocean, as part of Operation Ivy. It was the first full test of the Teller–Ulam design, a staged fusion device.
TESTING OF IVY MIKE H-BOMB :- http://festyy.com/wXEH0k
7.Mk-36 nuclear bomb – 10Mt
- The Mark 36 was a more advanced version of the earlier Mark 21 nuclear bomb, which was a weaponized version of the "Shrimp" design, the first "dry" (lithium deuteride) fuel thermonuclear bomb the United States tested, in the Castle Bravo thermonuclear test in 1954.
- The Mark 21 bomb was developed and deployed immediately after Castle Bravo, in 1955. The Mark 21 design continued to be improved and the Mark 36 device started production in April 1956.In 1957, all older Mark 21 bombs were converted to Mark 36 Y1 Mod 1 bombs. A total of 920 Mark 36 bombs were produced as new build or converted from the 275 Mark 21 bombs produced earlier.
- All Mark 36 nuclear bombs were retired between August 1961 and January 1962, replaced by the higher yield B41 nuclear bomb.
8.B53 (Mk-53) – 9Mt
- The B53 was the basis of the W-53 warhead carried by the Titan II Missile, which was decommissioned in 1987. Although not in active service for many years before 2010, fifty B53s were retained during that time as part of the "hedge" portion of the Enduring Stockpile until its complete dismantling in 2011. The last B53 was disassembled on 25 October 2011, a year ahead of schedule.
- With its retirement, the largest bomb currently in service in the U.S. nuclear arsenal is the B83, with a maximum yield of 1.2 megatons.The B53 was replaced in the bunker-busting role by a variant of the two-stage B61 nuclear bomb.
- The Mk/B53 was a high-yield bunker buster thermonuclear weapon developed by the United States during the Cold War. Deployed on Strategic Air Command bombers, the B53, with a yield of 9 megatons, was the most powerful weapon in the U.S. nuclear arsenal after the last B41 nuclear bombs were retired in 1976.
9.Mk-16 (TX-16/EC-16) nuclear bomb – 7Mt
- The Mark 16 nuclear bomb was a large thermonuclear bomb (hydrogen bomb), based on the design of the Ivy Mike, the first thermonuclear device ever test fired. The Mark 16 is more properly designated TX-16/EC-16 as it only existed in Experimental/Emergency Capability (EC) versions.
- The TX-16 bomb was 5 ft 1.4 in (1.56 m) in diameter, 24 ft 8.7 in (7.54 m) in length, and weighed 39,000 to 42,000 lb (17,690 to 19,050 kg). Design yield was 6-8 megatons of TNT.
- The TX-16 was scheduled to be tested as the Castle Yankee "Jughead" device until the overwhelming success of the Castle Bravo "Shrimp" test device rendered it obsolete.
TESTING OF MK 16 :- http://festyy.com/wXEHtJ/
10.Mk-14 / TX-14 – 6.9Mt
- The Mark 14 nuclear bomb was a 1950s Strategic thermonuclear weapon, the first solid-fuel staged hydrogen bomb. It was an experimental design, and only five units were produced in early 1954. It was tested in April 1954 during the Castle Union nuclear test and had a yield of 6.9 Mt. The bomb is often listed as the TX-14 (for "experimental") or EC-14 (for "Emergency Capability"). It has also been referred to as the "Alarm Clock" device though it has nothing to do with the design by the same name proposed earlier by Edward Teller and known as the Sloika in the Soviet Union.
- The version tested at Castle Union used a RACER IV primary, which resulted in 5 Mt of its total yield coming from fission, making it a very "dirty" weapon.
FOR THE NUCLEAR EXPLOSION COMPARSION , I STRONGLY REFFERED YOU GUYS TO MUST WATCH THE VIDEO GIVEN IN THE LINK
http://festyy.com/wXEHj2
IF YOU LIKE OUR POST PLEASE GIVE YOUR IMPORTANT FEEDBACK IN THE COMMENT BOX AND FOLLOW US ON OUR SOCIAL HANDLES.
THIS WILL HELP US TO GROW AND IMPROVE OUR FUTURE POST.
THANK YOU
IF YOU LIKE OUR POST PLEASE GIVE YOUR IMPORTANT FEEDBACK IN THE COMMENT BOX AND FOLLOW US ON OUR SOCIAL HANDLES.
THIS WILL HELP US TO GROW AND IMPROVE OUR FUTURE POST.
THANK YOU
Top 10 Nuclear Powers | Most Destructive Nuclear Weapons
 Reviewed by Top 10 Picks
on
November 09, 2018
Rating:
Reviewed by Top 10 Picks
on
November 09, 2018
Rating:
 Reviewed by Top 10 Picks
on
November 09, 2018
Rating:
Reviewed by Top 10 Picks
on
November 09, 2018
Rating:










No comments: